What is predictive maintenance (PdM)?
Predictive Maintenance is a type of condition-based maintenance technique that makes use of sensors attached to the equipment. This helps collect asset-performance data and help predict when a maintenance task needs to be carried out thus avoiding failures.
With Predictive Maintenance, maintenance work is only carried out when warranted thereby saving costs as compared to other types of maintenance.
Types of Predictive Maintenance
1. Vibration analysis
2. Acoustic analysis (sonic and ultrasonic)
3. Infrared Analysis
Unlike the first two types of vibration and oil analysis, this type of predictive maintenance analysis uses temperature as an indicator. Infrared analysis includes problems such as overheating, cooling, air flow or motor stress.

How does predictive maintenance work?
In order to effectively implement predictive maintenance, one needs to define the normal parameters. These parameters are then compared to the condition of an asset.
This essentially develops a ‘control’ when collecting conditional data through the sensor attached to the equipment. This helps measure abnormalities based on that. A work order is then created to tackle a given condition upon the prediction suggested by the data from the sensor.
PdM across different industries and their examples
Food Industry
Power Industry
Oil and Gas Industry
Hospitality Industry
Manufacturing Industry
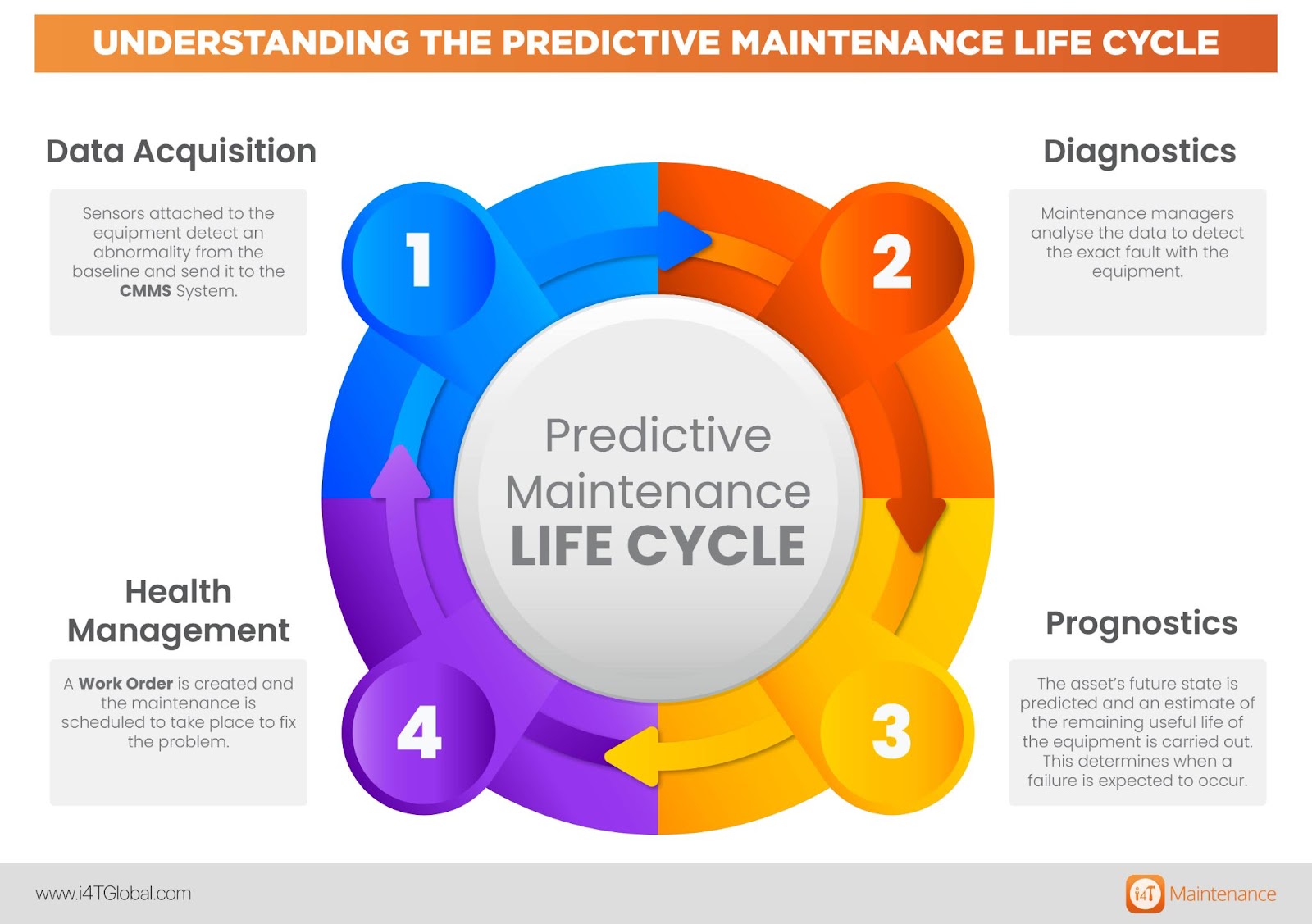
Understanding the Predictive Maintenance Life cycle
Predictive Maintenance life cycle is essentially all the steps that take place from asset monitoring to taking the corrective action.
Predictive Maintenance life cycle involves the following steps:
- Data Acquisition: Sensors attached to the equipment detect an abnormality from the baseline and send it to the CMMS System.
- Diagnostics: Maintenance managers analyse the data to detect the exact fault with the equipment.
- Prognostics: The asset’s future state is predicted and an estimate of the remaining useful life of the equipment is carried out. This determines when a failure is expected to occur.
- Health Management: A Work Order is created and the maintenance is scheduled to take place to fix the problem.
Conditional Monitoring technology and predictive maintenance techniques
Applying predictive algorithms
Predictive maintenance is not possible without the right algorithms. It will be right to say that this is most certainly the toughest part of setting up.
Applying predictive algorithms requires consideration of many variables, how each of them are connected and how changing one impacts the other. This helps make the right predictions when the equipment might fail. This also calls for several iterations based on asset history, observations, analysis and multiple sensors. These iterations help create the predictive model for the maintenance to take place.
The role of IoT technology
Predictive maintenance machine learning and AI
Artificial intelligence, in particular machine learning, allows systems to be trained to provide specific responses based on certain queries, commands or situations.
In the context of predictive maintenance, it serves as a powerful tool to understand data and improve operational performance. ML gives maintenance managers the ability to connect CMMS to process large volumes of diverse and complex data inputs from IoT devices. This data is then turned into useful information to understand asset health and make Predictive Maintenance recommendations.
Pros and Cons of Predictive Maintenance
There is no maintenance strategy that doesn’t come with its drawbacks. Predictive Maintenance too has its upsides and downsides. Let’s delve deeper into these.
| Pros of Predictive Maintenance | Cons of Predictive Maintenance |
| Improves asset’s reliability. | Has a higher up-front cost to set up and install. |
| Reduces asset’s downtime and increases productivity. | Managers analysing condition-based data require specialised knowledge. |
| Maintenance can take place while the asset is still running thereby avoiding any disruption. | Requires specific equipment and software to provide accurate data. |
| Provides a real-time view on asset condition. | Set up and installation can be time consuming and complex. |
| Optimises use of spare parts. | |
| Minimises time taken to carry out maintenance work |
Overall, the pros are more than the cons when using Predictive Maintenance and the ROI significantly increases over time.
Predictive maintenance analytics and calculating the ROI to maintain the quality
While Predictive maintenance setup and installation require significant investment, the benefits soon begin to outweigh the costs.
In its most simplistic form, the formula to calculate the ROI of Predictive Maintenance is as follows:
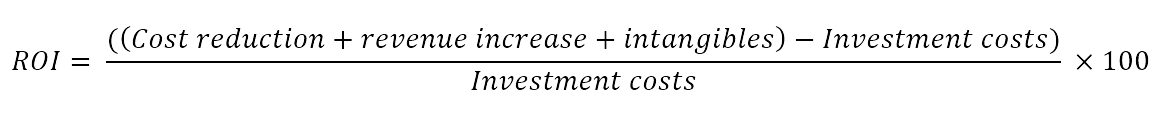
In order to calculate the Return on Investment with Predictive Maintenance it’s important to understand the factors that come into play here.
- Cost reduction: The cost is cut down in a number of ways. These include reduction in downtime, unplanned repairs, spare parts, labour costs, replacement costs and over-maintenance.
- Revenue increase: The revenue is increased in terms of equipment availability, more production, higher quality and efficiency.
- Intangibles: Some benefits cannot be quantified. So we give them weights. These include efficiency, process improvement and risk reduction.
- Investment cost: PdM can be expensive. It makes sense to take into account all the costs such as initiation, solution development, purchase, installation, implementation and governance.

Combining predictive maintenance with CMMS software
The data generated for predictive maintenance purposes is of limited use if it is not linked to a Computerised Maintenance Management System. CMMS is the core of Predictive Maintenance for a number of reasons.
- CMMS provides the base to get started with PdM: With the data collected and stored in the CMMS software, managers are able to analyse trends. They are also able to make predictive decisions in an efficient and accurate manner.
- CMMS helps automate Work Orders: As soon as the sensor attached to the equipment sends an alert, CMMS generates a work order. Today, modern CMMS are capable of doing this to tackle the problem with the use of Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence.
- CMMS helps turn data into information: Easy interpretation of the collected data allows Maintenance managers to manage the health of an asset better.
- CMMS allows data sharing and reporting: CMMS is able to pull together all data in one place. This allows simple report generation further helping with decision making and taking corrective action.
Preventive vs Predictive maintenance
When you are looking to streamline maintenance tasks, it can be confusing as to which maintenance method should be used. The difference between Preventive and Predictive Maintenance lies in the purpose or end-goal that a manager wishes to achieve.
Both methods make use of data driven technologies to identify faults and make decisions. However, the nature of data collected is not the same.
| Preventive Maintenance | Predictive Maintenance |
| Preventive maintenance is scheduled on a regular basis to keep assets working optimally and avoid downtime. | Predictive maintenance is generally based on asset condition and is carried out only when needed. |
| Managers need access to manufacturer recommendations and best practices for maintaining an asset. | Managers need access to data that indicates the current condition of an asset in order to predict potential issues. |
| This is a proactive maintenance strategy which is aimed at extending an asset’s useful life. | Predictive maintenance addresses challenges of both reactive and preventive maintenance without running to failure. |
| The maintenance work is scheduled over weekly, monthly or yearly timelines and thus costs more in unnecessary prevention activities. | Work is scheduled based on the requirement as identified by condition assessment. It can result in 10 times more ROI due to cost reduction. |
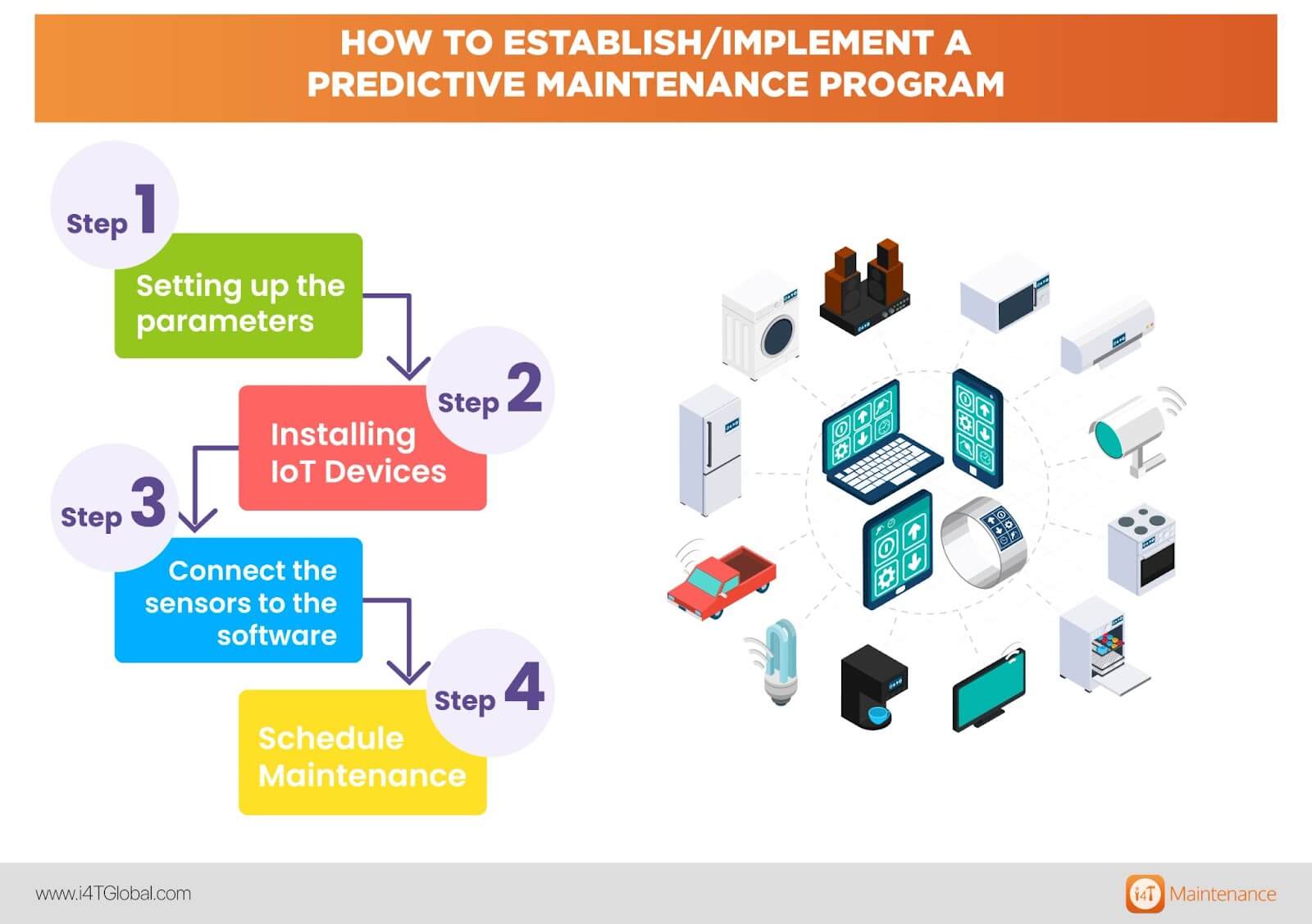
How to establish/Implement a predictive maintenance program
Before any predictive maintenance work is performed, management’s buy in is important in terms of ROI. Field Service Maintenance staff is trained to carry out the predictive maintenance work. In addition, operators are trained to use the IoT technology. This sets the groundwork for predictive maintenance on the facility itself.
There are 4 steps to implementing a Predictive Maintenance program.
Step 1: Setting up the parameters
Step 2: Installing IoT Devices
Step 3: Connect the sensors to the software
Step 4: Schedule Maintenance
Parting Thoughts
While Predictive Maintenance is one of the best strategies so far, it might not be the right fit for every organisation.
However, those that have already mastered less complex maintenance methods and have the budget, Predictive Maintenance can provide a great ROI.
Hot off the press!

With our cutting-edge technology and in-depth knowledge of how the Field Service Management sector operates, the i4TGlobal Team loves to share industry insights to help streamline your business processes and generate new leads. We are driven by innovation and are passionate about delivering solutions that are transparent, compliant, efficient and safe for all stakeholders and across all touch points.