The success of any business depends on how efficiently its assets and resources perform. This is exactly what a well-defined maintenance management process helps with.
From residential and commercial buildings, to hotels and restaurants, shops, factories and other facilities, maintenance management plays a vital role. It helps managers with budgeting for resources, scheduling work orders, meeting compliance requirements, optimising work and improving safety for occupants.
It gives facility managers the control over unforeseen situations, such as broken equipment or workplace accidents. This is done by providing them with the necessary insights to regularly carry out preventive maintenance or corrective maintenance.
Let’s now delve a bit deeper into the different activities involved in carrying out maintenance management. We will also draw a comparison between Computerised Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS) and Enterprise Asset Management systems (EAM). Finally, we will look at why automating the maintenance management process can help your business reap greater rewards down the line.
What is Maintenance Management?
Maintenance management is the process of optimising a company’s assets and resources. It helps with:
- Reducing repair costs and downtime.
- Increasing operational efficiency and productivity.
- Ensuring compliance and occupant’s safety.
Maintenance management does not involve just the system itself, but it’s a whole set of best practices to be followed. To carry it out successfully, a group of personnel is trained. They are responsible to maintain the assets and resources in the most optimal way.
The maintenance management process needs to be tailored to the specific needs of an organisation. It also needs to be linked to the type of maintenance you are undertaking.
The process has to be monitored on an ongoing basis. This helps identify areas of improvement so adjustment to the program can be made accordingly.
Why is Maintenance Management Important?
Maintenance management is critical to ensure that your facilities are always performing at their best. This means minimum downtime, highest productivity, zero errors and lowest costs.
Without an effective maintenance management program, your business might run into several risks. These risks can be in the form of delayed product delivery to the market. You also risk losing the customer’s trust.
- When your company’s assets and resources are maintained in the most optimal way, the chances of downtime is reduced. Hence, effective maintenance management improves the reliability and availability of your assets round the year.
- Maintenance management helps reduce a company’s repair and maintenance costs. With a CMMS, your processes are closely tied to your maintenance program, like preventive maintenance, predictive maintenance or condition-based maintenance. This ensures that assets and resources never reach a point where they have to be repaired on an emergency basis.
- Maintenance management improves operational efficiency of the plants and the facilities. At the same time it helps with minimising human error ensuring quantity targets are met.
- Maintenance management improves customer satisfaction and reduces complaints regarding manufactured goods or service delivery.
- Maintenance management systems provide historical data from past maintenance work carried out. This helps managers make more informed decisions with respect to costs, scheduling and productivity.
What are the Objectives that Maintenance Management Serves?
1. Controlling Costs
Maintenance managers have limited budgets to work with. This means they need to allocate maintenance budgets in the most efficient ways. Not doing so can make maintenance budgets sprawl out of hand. Managers might be left with no money to maintain business critical equipment and facilities.
With the right budgeting insights, maintenance managers have more process transparency. They are better able to budget for unforeseen situations. They are also in a position to purchase inventory at a lesser price and pay for maintenance rather than for costly repairs.
2. Scheduling Work Orders
Ensuring the best technician is available for work when needed, requires significant planning. With the help of maintenance management, managers are able to control how work flows from start to finish. This information helps them prioritise maintenance work and allocate resources accordingly.
3. Meeting Regulatory Compliance Requirements
4. Prevents Loss Due to Down Time
One of the most important objectives of carrying out maintenance management is to ensure that every system in the facility is working optimally, round the clock.
Downtime on the facility creates bottlenecks and tends to have a ripple effect, impacting all departments and personnel.
The less the downtime, the more will be the productive time on the facility and the higher will be the revenue.
5. Prolongs Asset’s Life
With a maintenance management program in place, regular wear and tear of the equipment is predicted before it happens. This prevents it from turning into a bigger issue down the road.
6. Provides Insights for Decision Making
Maintenance management is an ongoing process. Hence managers need to keep record of their work orders, assets and resources all the time.
Data collected this way over a long period of time is then able to show operational trends. This gives managers insights into what worked and what are the areas that need to be improved.
It also gives managers vital information on:
- How much inventory to maintain
- What are the areas where costs can be curbed
- Which technicians are best trained to perform a certain nature of work orders and so on
7. Improves Safety of the Occupants
Equipment malfunctions can put the health and lives of occupants at a serious risk. It can also sink costs, affect business reputation and end up with property owners paying heavy fines in non-compliance.
When maintenance management is carried out the right way it enhances the safety of:
- The people occupying the premises
- Those carrying out the work
- The ones managing the work
- People who are simply visiting the facility
What are the Different Types of Maintenance Management?
1. Run-to-Failure Maintenance
Run-to-failure is the most basic kind of maintenance management. In this, the equipment is allowed to run until it eventually breaks down and is replaced. An example could be of a light bulb that remains in use until it reaches the end of its useful life.
However, in a more complex setting, this is not the preferred kind of maintenance technique. This strategy can result in expensive reactive maintenance costs to replace entire systems and equipment.
2. Time-Based Maintenance
Time-based maintenance is carried out at regular intervals, irrespective of what the condition of the system or equipment is. For example, replacing the filters of an air conditioner or replacing the batteries of a smoke alarm every six months,
This kind of maintenance ensures problems can be caught before they happen and action is taken accordingly. However, this is not always the most cost effective type of maintenance method.
3. Condition-Based Maintenance
4. Predictive Maintenance
Another advanced type of maintenance is predictive maintenance. It uses a combination of condition-based maintenance, machine learning, and other technologies to predict when a system might fail.
This provides an early warning to maintenance managers. They can then act proactively to take corrective action before the issue actually arises.
5. Prescriptive Maintenance
Prescriptive maintenance not only identifies the issue beforehand but also suggests a calculated solution or advisable course of action to take.
This is the most advanced kind of maintenance available today, requiring minimum human intervention.
How can CMMS Software Help?
CMMS or Computerised Maintenance Management Software can simplify and fast track your processes.
CMMS can help automate tasks and store information that can be used to perform the job more effectively. The information provided by CMMS can also be used to make informed decisions with respect to asset, time and resource allocation.
Choosing the right CMMS doesn’t have to be tricky. A CMMS software is highly intuitive and can help managers perform tasks such as:
Who should have Access to your CMMS?

The more people have access to your CMMS, the more empowered your teams will be and the better will be the operational workflow.
Some of the individuals who can benefit by having access to your CMMS include:
- Maintenance manager: This is the person who acts as the system admin. He/she is responsible for overseeing every aspect of the maintenance work going through the system.
- Operations manager: These individuals are responsible for improving workflow efficiency, allocate budgets, parts procurement and prepare audits. They need access to check the overall operational performance.
- Data engineers: Personnel in this department analyse the CMMS data and prepare meaningful reports for analysis and decision making.
- Inventory managers: With complete access to the CMMS, inventory managers are able to keep track of inventory levels. When it is going below the desired levels, managers are notified and take action.
- Compliance manager: These individuals are responsible for making sure all the work is carried out as per the regulations. This includes work is carried out as per the health and safety guidelines and SOPs are followed.
- Contractors and technicians: These individuals need to be notified when a work order is created and assigned. They need to have all the information to carry it out as per the requirements.
- Production managers: These are individuals that work directly with the equipment on the factory floor. They are the first ones to identify and report any malfunctions that need to be taken care of. They can prompt maintenance managers to create a work order.
- Top management: The individual in the leadership position of a company needs access to your CMMS. They are the decision makers and need to keep an eye on KPIs, goals, team performance and so on.
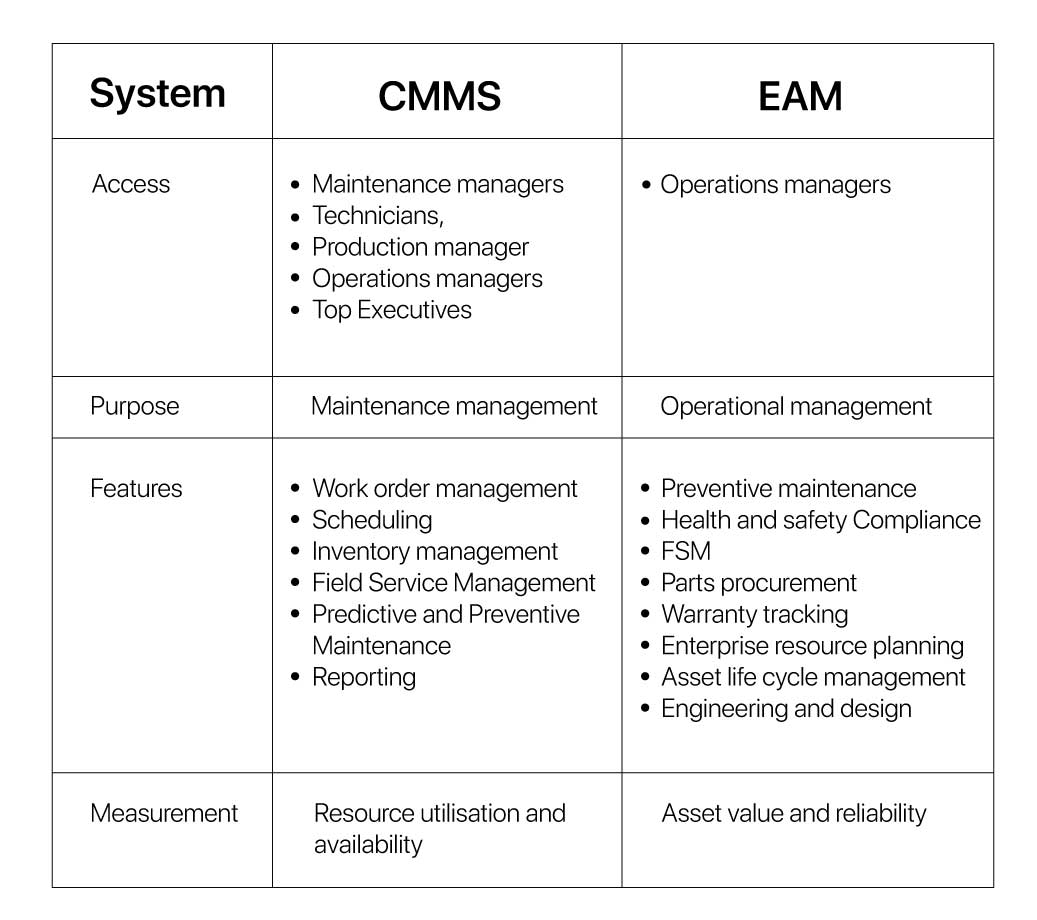
CMMS vs Enterprise Asset Management (EAM)
The Role of i4T Maintenance Software Solution
i4T Maintenance is a powerful CMMS solution that has already been tested and validated by the property and facility management sectors.
i4T Maintenance allows Authorised Field Service Agents to streamline processes to operate efficiently. It helps increase productivity, cut costs and run facilities better.
It is highly versatile and caters to the maintenance management needs of businesses of all shapes and sizes. Register today to see if it’s the right fit for your business.
Hot off the press!

With our cutting-edge technology and in-depth knowledge of how the Field Service Management sector operates, the i4TGlobal Team loves to share industry insights to help streamline your business processes and generate new leads. We are driven by innovation and are passionate about delivering solutions that are transparent, compliant, efficient and safe for all stakeholders and across all touch points.









